As of 2025, prompt engineering isn’t just a niche skill, it’s a career path. The explosion of AI tools has led companies to hunt for individuals who know how to speak the language of machines. From startups building AI writing tools to corporations optimizing internal workflows, prompt engineers are in high demand. Why? Because even the most powerful AI models are only as good as the instructions they’re given.
Prompt engineering helps businesses reduce costs, increase output quality, and enhance user experiences. Developers rely on prompt engineers to optimize AI APIs. Content creators depend on well-designed prompts to churn out high-quality blogs, ads, and social media posts. And entrepreneurs are using custom prompts to build automated business assistants, legal advisors, and more.
As models evolve, so do the possibilities, and the complexity. That’s why learning prompt engineering in 2025 isn’t just a smart move; it’s a future-proof investment in your career.
Applications Across Industries
Here’s the fun part: prompt engineering isn’t confined to one field. Its applications are as diverse as the internet itself.
- Marketing: Generate social media calendars, email sequences, and SEO-optimized content.
- Education: Build AI tutors, quiz makers, and automated feedback systems.
- Healthcare: Summarize patient notes, extract medical insights, and simulate patient interactions.
- Law: Draft legal documents, conduct research, and analyze case data.
- Software Development: Generate code snippets, debug, and document APIs.
This wide usage means no matter your background, writer, teacher, marketer, coder, you can integrate prompt engineering into your workflow and amplify your productivity.
Understanding the Basics Before You Begin
Foundation of AI and Language Models
Before jumping into prompt writing, you need to understand the engine under the hood: large language models (LLMs). These are AI systems trained on massive text datasets to predict the next word in a sentence. Models like GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini use transformer architecture to generate human-like text based on input prompts.
Here’s a crash course in what you need to grasp:
- Tokens: AI models don’t read words; they read tokens. A word like “prompt” might be one token, but “engineering” could be split into two.
- Training: Models learn patterns by analyzing billions of sentences. They’re not “thinking”—they’re predicting.
- Context Window: Each model has a limit to how much it can remember from your prompt. GPT-4, for instance, can process thousands of tokens at a time.
Understanding these mechanics helps you tailor your prompts so the AI doesn’t get overwhelmed, go off-topic, or produce bland results.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) Overview
Prompt engineering is deeply connected to NLP, Natural Language Processing. This is the field of AI that focuses on how machines understand, interpret, and generate human language. NLP tasks include sentiment analysis, text summarization, translation, and question answering.
Why does this matter? Because prompt engineering is basically NLP in action. The better your understanding of NLP concepts like context, entity recognition, and intent, the more powerful your prompts will become. This isn’t about becoming a data scientist. It’s about gaining just enough understanding to use AI effectively.
How Prompts Interact with AI Models
When you send a prompt to an AI model, it processes it word by word, considering what it has learned during training. Based on your prompt’s structure, tone, and clarity, the model predicts the most likely response.
Think of it like programming, but in plain English.
Let’s say you prompt an AI with:
“Write a funny poem about pizza using Shakespearean language.”
You’re guiding it with:
• Tone: Funny
• Style: Shakespearean
• Topic: Pizza
The AI follows your blueprint. If you’re vague, like “Write about pizza”, you’ll get generic content. If you’re specific and smart, you’ll get gold.
Knowing how to control AI responses is the entire point of prompt engineering. The sooner you grasp that, the sooner you’ll start creating content that stuns, sells, or solves problems.
The Tools You’ll Need to Start
AI Platforms You Should Get Familiar With
To practice prompt engineering effectively, you’ll need access to LLM platforms. Here are the big names to get comfortable with:
- ChatGPT by OpenAI (GPT-4.5 or GPT-4 Turbo)
- Claude by Anthropic
- Gemini by Google
- Perplexity AI for research-based prompts
- Notion AI for productivity prompts
Each platform has its strengths. For instance, GPT-4 is great for creativity and coding. Claude shines in writing assistance and long-form memory. Gemini is excellent at connecting real-time data with conversation.

Don’t just use one. Experiment across all platforms to get a feel for how differently they respond to the same prompt.
Also Read: Top Use Cases of Prompt Engineering in AI Tools Like ChatGPT & Midjourney
Recommended Devices and Software
You don’t need a supercomputer. But a reliable laptop or tablet and a high-speed internet connection are essential. Some cloud tools like OpenAI Playground or Google Colab can be handy if you want to integrate code or customize models.
Helpful software and extensions:
- Prompt engineering notebooks (like Notion or Obsidian)
- Chrome extensions like AIPRM, WebChatGPT, or FlowGPT
- APIs if you want to test prompts at scale
The setup isn’t complicated, but consistency is key.
Browser Extensions and Prompt Tools
To really level up your prompting skills, tools like these can help:
- PromptHero: A marketplace and library for great prompts.
- PromptBase: Sell or buy effective prompt templates.
- FlowGPT: Community-driven prompt sharing platform.
- Zapier or Make: To automate prompt-driven workflows.
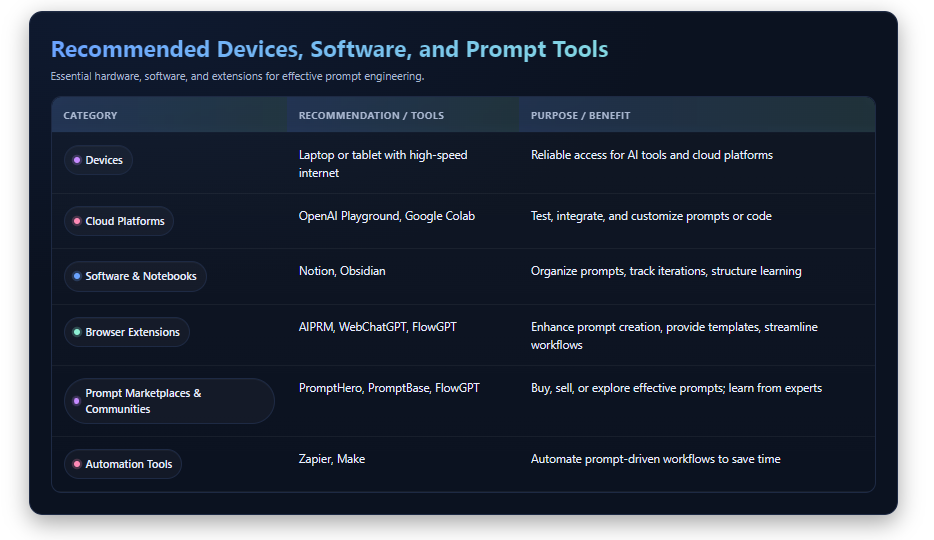
These tools reduce guesswork, inspire better structure, and give you templates to start with. Plus, they let you peek at what expert prompt engineers are already doing.
Key Concepts Every Beginner Must Master
Prompt Structure and Formatting
Before crafting killer prompts, you need to understand structure, it’s the backbone of effective communication with AI. A good prompt is like a well-written recipe: clear, concise, and sequenced. Just like you wouldn’t start a cooking guide with “add salt” before introducing the dish, you shouldn’t throw the AI into a task without setting the scene.
Let’s break it down:
- Instruction-Based Format: “Summarize the following paragraph…”
- Input-Output Format: “Input: [text] | Output: [desired result]”
- Role-based Prompts: “You are a legal advisor. Draft a contract…”
Each of these structures helps the AI know how to behave. The more specific you are, the better your result. Want a poem? Ask for one. Want it to rhyme? Say that. Want it short? Mention word count.
Use formatting too:
- Bold headings (with markdown or formatting symbols)
- Bullet points for lists
- Clear separators like “###” or “—” if feeding multiple inputs
Bad prompt: “Write something about dogs.”
Better prompt: “Act as a pet expert. Write a 200-word, fun, and informative article about Labrador Retrievers as family pets.”
The difference? One is vague; the other is a complete blueprint.
Temperature, Tokens, and Model Parameters
Every AI model has settings under the hood, like the knobs and dials on a stereo. You don’t need to mess with them every time, but understanding them gives you an edge.
- Temperature: Controls creativity. Lower (0.2) = precise, factual. Higher (0.8+) = more imaginative and unpredictable.
- Max Tokens: Controls output length. Each word = ~1.3 tokens.
- Top_p (Nucleus Sampling): Another creativity lever that controls the randomness of outputs.
- Frequency Penalty: Reduces repetition.
- Presence Penalty: Encourages exploring new ideas.
Example:
- A legal contract prompt? Keep temperature at 0.2.
- A fantasy story prompt? Boost it to 0.8+.
Understanding these lets you tailor responses for precision or playfulness, depending on what you need.
Few-shot, One-shot, and Zero-shot Prompting
These aren’t just buzzwords, they’re fundamental to how AI understands your intent.
Zero-shot prompting means giving a direct instruction with no examples. It’s fast but may lack precision.
“Translate the following text into Spanish.”
One-shot prompting provides one example.
“Example: Hello → Hola. Now translate: Goodbye.”
Few-shot prompting includes multiple examples to train the model inline.
“Hello → Hola. Good morning → Buenos días. Please translate: How are you?”
Few-shot prompting works like giving the AI a mini lesson before it performs a task. The better your examples, the better your output.
Using these styles effectively can drastically improve consistency and tone, especially for tasks like data extraction, customer support scripts, or generating creative content.
Building the Right Learning Mindset
Mistakes Are Lessons, Not Failures
Let’s get one thing straight: your first 50 prompts will probably suck. And that’s perfectly fine. Prompt engineering is an iterative art, it’s about refining your input based on what works and what doesn’t.
Don’t get frustrated if a model misunderstands your request. Instead, ask:
- Was I too vague?
- Did I give enough context?
- Could the instructions be more specific?
Think of it like training a dog. It takes time, feedback, and treats (in this case, editing) to shape behavior.
The beauty of AI prompting is that feedback is instant. You can revise and resubmit in seconds. Use this loop to your advantage. Keep a journal or Notion doc of “what worked” and “what flopped.”
Treat mistakes as stepping stones. The only real failure is giving up after the first weird answer.
Curiosity Over Complexity
Here’s a secret: the best prompt engineers aren’t the ones who use the fanciest jargon. They’re the ones who stay curious.
Got a weird idea for a story where Napoleon is a tech CEO? Try it. Wonder what happens if you ask the AI to generate dialogue like Tarantino? Test it. The more curious you are, the faster you learn the boundaries (and hidden tricks) of the models.
Complexity isn’t the goal, clarity is. Start simple:
- “Write a poem in the voice of a pirate.”
- “Summarize this article in 3 bullet points.”
- “Explain quantum physics like I’m 10.”
Eventually, curiosity leads to confidence. Confidence leads to mastery.
Practicing Over Perfection
Want to get good at prompt engineering? Practice daily.
Set aside 15–30 minutes a day to:
- Choose a random topic.
- Write a prompt.
- Analyze the response.
- Refine and try again.
You can even create a challenge for yourself. For example:
- Day 1: Generate a haiku
- Day 2: Write a meal plan
- Day 3: Simulate a job interview
- Day 4: Build a customer support dialogue

Platforms like FlowGPT or PromptHero let you see what others are doing. Copy, remix, test. It’s like learning to DJ with other people’s beats.
Forget perfection. Focus on progress.
Step-by-Step Prompt Engineering Roadmap (2025 Edition)
Month 1: Understanding AI Fundamentals
Your first month should be all about building a rock-solid foundation. Don’t rush into writing complex prompts without understanding how AI models think. Instead, focus on the theory, the tech, and the behavior of large language models (LLMs).
Here’s what to cover in Month 1:
- Learn the history of LLMs – Study how models evolved from GPT-1 to GPT-4 and beyond. Understand what makes transformer models special.
- Understand basic AI concepts – Learn terms like supervised learning, unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning, and fine-tuning.
- Play around with models – Try ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and others. Observe how each responds to similar prompts.
- Watch beginner tutorials – YouTube is packed with content from prompt engineers, AI researchers, and tech creators.
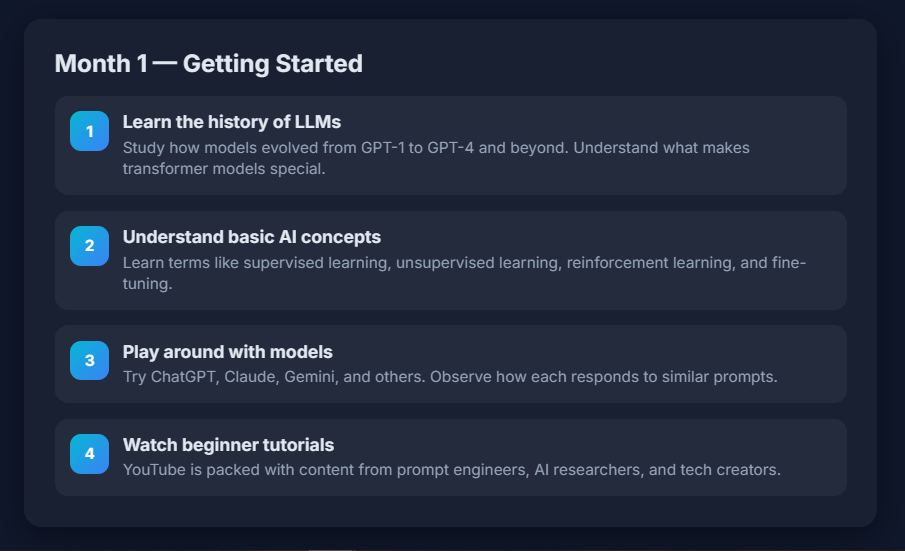
Your goal in Month 1 isn’t mastery, it’s familiarity. You should start to understand:
- What AI models can and can’t do.
- How AI interprets tone and intention.
- The limits of accuracy and context windows.
Tip: Keep a learning journal or digital notebook with your insights. Document your “aha” moments, prompt failures, and successful tweaks. This will become your reference guide as you grow.
Month 2-3: Practicing Simple Prompts
Now that you’ve got your basics down, it’s time to dive into practice. These two months are for trying as many prompts as possible across different tasks. Think of this phase like going to the gym, you’re building your muscle through repetition.
Types of prompts to master:
- Creative prompts: Storytelling, poetry, and humor writing
- Instructional prompts: Summarization, rephrasing, explaining
- Conversational prompts: Simulating dialogue, FAQs, customer support
- Technical prompts: Code generation, documentation, data analysis
Daily exercise plan:
1. Choose a task (e.g., summarize an article).
2. Write a basic prompt.
3. Review the result, was it what you expected?
4. Edit the prompt and retry.
5. Note what changed and why.
Example:
- First attempt: “Summarize this article.”
- Refined prompt: “Summarize the following article in 3 key bullet points for a high school student audience.”
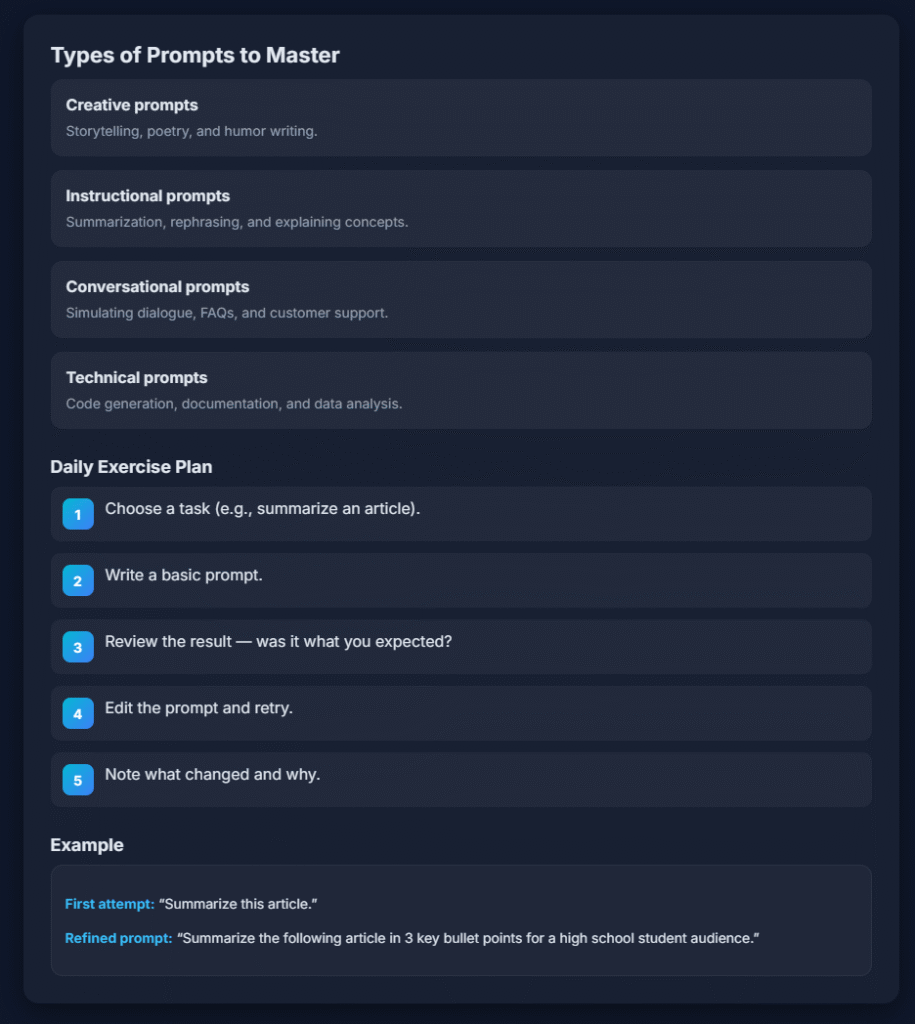
Notice how a single tweak can shape the AI’s tone and depth. This is the true craft of prompt engineering, learning how to adjust dials with words.
Tools to use during this phase:
- Prompt logging tools like Notion or Airtable
- Prompt testing environments like OpenAI Playground
- Prompt libraries like PromptHero, AIPRM, or FlowGPT
By the end of Month 3, you should be comfortable writing prompts for common use cases, know how to fix poor responses, and feel confident about structuring your tasks.
Month 4-6: Designing Prompts for Real-World Use Cases
Now it’s time to go pro. In this phase, your focus should shift from learning to building. Start designing prompts that solve real problems, automate workflows, and add value.
Projects you can work on:
- Content Creation Pipeline: Automate blog writing, outlines, SEO meta descriptions.
- Customer Service Chatbot: Train prompts to simulate responses to FAQs.
- Coding Assistant: Design prompts that generate Python scripts or debug code.
- E-commerce Prompts: Write product descriptions based on raw product data.
- Virtual Assistant: Create a prompt-based daily planner or meeting summarizer.
Best practice:
- Start simple, then layer complexity.
- Always include context, don’t make the AI guess.
- Use prompt chaining: feed the output of one prompt into another.
Prompt chaining example:
1. Prompt 1: “Summarize this article about climate change.”
2. Prompt 2: “Convert the summary into an Instagram caption.”
3. Prompt 3: “Generate 5 hashtags for this post.”
See how one idea evolves across multiple prompts?

Also, begin documenting your prompt flows. You can use tools like Whimsical, Miro, or even Canva to visualize how your inputs connect.
By the end of Month 6, you should have:
- A portfolio of working prompt-based projects.
- A refined understanding of prompt performance.
- A unique style or niche where your prompting skills shine.
Common Prompting Mistakes and How to Fix Them
Overcomplicating the Language
It’s easy to assume that complex problems need complex prompts, but the truth is, simplicity wins. A common beginner mistake is stuffing too much into one sentence or using jargon that the AI misinterprets.
Bad prompt:
“Considering the juxtaposition of temporal narrative arcs, describe in multifaceted prose the psychological journey of the protagonist within the emotional framework of 20th-century post-war literature.”
Better prompt:
“Describe the emotional journey of the main character in a 20th-century post-war novel, using rich, literary language.”
Fix: Break long sentences into parts. Be specific but not convoluted. AI is smart, but it prefers clarity over cleverness.
Misunderstanding Model Capabilities
Many new prompt engineers overestimate or misunderstand what AI can do. Yes, it’s powerful, but it’s not psychic.
For example:
• It can summarize a PDF but only if you feed it the content (unless it has file upload access).
• It can simulate a conversation but doesn’t actually understand emotional nuance like a human would.
• It can generate code, but complex programming problems still require debugging by a real developer.
Solution: Always experiment. Don’t assume, test. Ask yourself:
• Does the model have access to what I’m referencing?
• Am I expecting an opinion when I should be getting facts?
• Did I define the scope clearly?
Forgetting the Role of Context
AI models thrive on context. If your prompt is ambiguous, your results will be too.
Instead of: “Write a headline.”
Try: “Write a headline for a digital marketing blog post about the benefits of using AI tools in content writing. Make it catchy and under 12 words.”
Context is everything:
• What is the user trying to do?
• Who is the audience?
• What tone should the output have?
Even adding a sentence like “You are an expert UX writer” can massively influence the style and quality of the response.
Best Resources to Learn Prompt Engineering
Free Courses and YouTube Channels
One of the biggest perks of learning prompt engineering in 2025 is that you don’t need a formal degree, just a good internet connection and curiosity. There are countless free resources that break down the fundamentals and advanced strategies of prompt engineering.
Here are top picks to get started:
Free Courses:
• OpenAI’s Prompt Engineering Guide – Updated frequently with new techniques and real-use cases.
• DeepLearning.AI’s “ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers” – An excellent starting point if you want hands-on instruction.
• Fast.ai Forum Discussions – Not a formal course, but invaluable insight from active developers and AI users.
• LearnPrompting.org – A community-driven guide with clear examples and exercises.
• PromptHero Academy (Free Modules) – Offers prompt templates and breakdowns from top creators.
YouTube Channels:
• AI Explained – Covers LLMs, prompt techniques, and AI news in layman’s terms.
• Data School – Offers practical AI implementation tutorials.
• Fireship – High-speed overviews that help you understand prompt concepts fast.
• Prompt Engineering Weekly – Bite-sized case studies and hacks.
• Matt Wolfe – Shares experiments, prompt challenges, and creative ways to use ChatGPT and Claude.
Tips for Learning from Free Content:
• Don’t just watch, try what you see.
• Keep notes of every new technique and result.
• Subscribe to channels that offer weekly updates and challenges.
These free tools are more than enough to get you skilled within months, especially if you pair them with daily practice.
Top Books and eBooks
While prompt engineering is a fast-evolving field, some experts have compiled their knowledge into guides that serve as great references. Books are excellent for deep dives, structured learning, and building a theoretical foundation.
Here are some highly recommended titles:
1. “The Art of Prompt Engineering with ChatGPT” by Nathan Hunter
Explains prompt formats, business use cases, and psychology of prompting.
2. “Prompt Engineering Guidebook” by Dennis Rothman
Deep NLP concepts, complete with diagrams and code examples.
3. “The Prompt Engineering Handbook” by Jim Clyde Monge
Easy-to-understand walkthroughs, suitable for beginners.
4. “Mastering ChatGPT for Prompt Engineering” by Dr. Lucian Lita
Academic but practical guide covering LLM theory and real-world prompting.
5. “Prompt Engineering for Everyone” (eBook, free from PromptHero)
Compact, community-driven guide.
How to Use These Books Effectively:
• Focus on one chapter a day.
• Try every example using ChatGPT or Gemini.
• Adapt examples to your personal projects.
Books give you frameworks. Real learning happens when you tweak those frameworks and apply them creatively.
Communities and Forums to Join
Prompt engineering is evolving so rapidly that communities often become more valuable than courses. These platforms keep you updated with trends, share effective prompts, and offer troubleshooting help.
Top communities in 2025:
• Reddit: r/PromptEngineering – Massive group with daily discussions, prompt reviews, and case studies.
• Discord Servers: Prompt Engineers United, FlowGPT Community – Ideal for networking, collaborations, and challenges.
• Twitter/X Spaces – Follow tags like #PromptEngineering, #ChatGPT, #LLMs for real-time news.
• LinkedIn Groups – Join professional AI and NLP communities to discover jobs and learning events.
• AI Stack Exchange – Ask technical questions about prompt behavior, model quirks, and prompt optimization.
Why Join a Community?
- You’ll learn from others’ mistakes and successes.
- You can get feedback on your prompts instantly.
- It’s easier to stay motivated and updated when you’re surrounded by peers chasing the same goal.
Pro Tip: Don’t lurk. Participate. Post your experiments, ask questions, and engage. The more visible you are, the faster you’ll grow.
Real-World Projects You Can Start With
Build a Chatbot
One of the easiest and most powerful projects for new prompt engineers is building a chatbot. Whether it’s for fun, customer service, or task automation, chatbots are the perfect sandbox to practice dynamic prompting.
Step-by-step to get started:
1. Choose a platform: ChatGPT, Botpress, Flowise, or Replika AI.
2. Decide on a niche: mental health coach, shopping assistant, event planner, etc.
3. Write your first system prompt: “You are a friendly event planner helping users find venues in New York.”
4. Create sample conversations and test how it responds.
5. Add fallback messages, clarifications, and user intent handling.
Want to take it further?
• Integrate it with a front-end UI.
• Deploy it on Telegram, Discord, or your website.
• Use Zapier to trigger emails, calendars, or CRM actions.
This project teaches you conversational flow, user context, and how to debug prompt logic effectively.
Create a Content Generator
Businesses, bloggers, and marketers are begging for AI-driven content. You can build a tool, or just a prompt pack, that automates this.
Project ideas:
• SEO blog generator
• YouTube title and script creator
• Email subject line tester
• Product description enhancer
Use prompt chaining:
1. Prompt 1: Keyword to Blog Outline
2. Prompt 2: Outline to Draft
3. Prompt 3: Draft to SEO Meta Description
Package these prompts in a Notion doc or a Zapier flow and you’ve got a functional mini SaaS!
Bonus Tip: Sell these prompts or tools on marketplaces like PromptBase or Gumroad.
Automate Business Workflows with Prompts
Every business has repetitive tasks, prompt engineering can automate many of them.
Examples:
• Summarize long emails or Slack threads
• Generate invoices or client proposals from form inputs
• Extract tasks from meeting notes
You can build these workflows using:
• OpenAI API + Zapier
• Notion AI + databases
• Google Sheets + GPT Extensions
Real-world automation teaches you to think in terms of inputs, context, and desired output. It also gives you portfolio-worthy results that can impress potential employers or clients.
Career Paths in Prompt Engineering
Freelancing vs. Full-Time Jobs
As of 2025, there are two primary paths you can follow as a prompt engineer: freelancing or full-time employment. Each has its pros and cons.
Freelancing:
Pros:
○ Freedom to work on different projects
○ Higher earning potential (per hour or project)
○ Remote-first, global clientele
Cons:
○ Unstable income (especially early on)
○ Requires self-marketing and lead generation
○ Often juggles multiple clients and deadlines
Full-Time Employment:
Pros:
○ Stable salary and benefits
○ Opportunities to collaborate with AI teams
○ More access to premium tools and datasets
Cons:
○ Less variety in tasks
○ May have slower growth if you’re not proactive
Best platforms to find work:
- Upwork, Fiverr, Freelancer.com – Great for early gigs
- Toptal, Contra, Braintrust – Higher-end freelancing jobs
- AngelList, AI-jobs.net, LinkedIn – Startups and remote job openings
Tip: Whichever route you take, keep building a portfolio. Show your value through real results, not just promises.
Earning Potential and Growth Trends
Prompt engineering is no longer a novelty, it’s a lucrative career path. With the demand for generative AI skills skyrocketing in 2025, prompt engineers are cashing in.
Here’s a breakdown of average earnings:
- Entry-level (0–1 year): $60,000–$90,000 annually
- Mid-level (2–4 years): $100,000–$150,000 annually
- Senior-level (5+ years or niche expertise): $160,000–$220,000+
- Freelancers: $50–$250 per hour depending on niche and complexity
Some AI consultants or solopreneurs are charging $1,000+ per project to design prompt systems for businesses, especially in marketing, HR automation, and content creation.
Factors affecting pay:
- Your niche (tech, education, legal, etc.)
- Whether you work with agencies, startups, or enterprise clients
- Your ability to communicate results and value clearly
- Your location (remote roles often adjust pay based on cost of living)
Prompt engineers who also know Python or can fine-tune models with APIs usually earn even more. The key is to continue upskilling and documenting your outcomes, clients and employers pay for results, not just prompt fluency.
Remote Opportunities and Global Demand
One of the most exciting aspects of this field? It’s truly borderless. In 2025, companies from all over the world are building AI-based tools and need people who know how to control and refine their models.
In-demand regions for prompt engineers:
- North America – AI startups and tech hubs in California, New York, and Toronto.
- Europe – AI firms in London, Berlin, and Amsterdam.
- Asia – Huge demand in India, Singapore, and Japan, especially for localization-focused prompting.
- Middle East & Africa – Emerging AI sectors in Dubai, Kenya, and South Africa.
Many job listings now include prompt engineering alongside skills like UX writing, software development, and digital marketing. It’s increasingly a “hybrid” role, embedded into creative, technical, and strategy teams.
If you want freedom, flexibility, and job security, this is the skill to have.
AI Startups and Prompt Roles
Startups are hotbeds for innovation, and they love prompt engineers. Many early-stage companies build MVPs (minimum viable products) around AI and need someone who can:
- Design user-friendly prompts
- Handle edge cases and misfires
- Optimize output consistency
- Improve UX through better prompt design
Prompt roles in startups include:
- Prompt Engineer / AI Trainer
- UX Prompt Writer
- Conversational AI Designer
- Content Automation Specialist
These roles often come with equity, which could be a huge payoff if the startup succeeds.
Where to find them:
- AngelList
- Wellfound
- Y Combinator job board
- Twitter/X job threads
Staying active in AI Discords, LinkedIn groups, and hackathons can also uncover opportunities before they’re posted.
How to Stay Updated in a Rapidly Changing Field?
Following AI Newsletters and Blogs
Prompt engineering evolves weekly. If you’re not keeping up, you’re falling behind. The best way to stay sharp? Subscribe to high-quality AI newsletters and blogs.
Recommended newsletters:
- Ben’s Bites – Daily digest of the top AI tools, news, and product launches.
- The Rundown AI – Trendy, bite-sized summaries and tool roundups.
- Prompt Engineering Daily – A curated list of new prompt techniques and LLM breakthroughs.
- Hugging Face Blog – Deep dives into model updates, API guides, and developer notes.
- OpenAI Developer Blog – Must-read updates from the creators of ChatGPT.
Set aside 10 minutes each morning to skim your inbox and click what interests you. It’s like investing in your own stock value every day.
Attending Conferences and Meetups
IRL and virtual events are where the AI magic really happens. You’ll learn more in one afternoon with experts than in a week of Googling alone.
Top AI and prompt-focused events:
- AI Expo North America
- PromptCon
- OpenAI DevDay
- LangChain + Pinecone Hackathons
- AI in Business Summits
Don’t just attend, engage. Ask questions, network, and maybe even present a project.
If you’re shy, start with smaller online meetups or Twitter Spaces. They’re casual, frequent, and surprisingly valuable.
Experimenting with New Tools and Features
Every week, there’s a new AI tool, API, or plugin. Many of these change how prompting works, or open doors to whole new workflows.
Some cool tools in 2025:
- LangChain – For chaining and memory in prompts.
- LlamaIndex – To build custom knowledge bases.
- AutoGPT and BabyAGI forks – Automating prompt pipelines.
- AgentOps – AI agent debugging and prompt logging.
Tip: Don’t overwhelm yourself. Choose one new tool each month. Play with it. Watch demos. Write a mini project using it. Rinse and repeat.
Growth doesn’t come from watching others experiment, it comes from your own trial and error.
Ethical Prompt Engineering
Bias in Prompts and How to Handle It
Large language models reflect the biases of the data they were trained on. As a prompt engineer, you must be aware of this. A poorly written prompt can reinforce stereotypes or unintentionally exclude certain groups.
Example of biased prompt:
- “Write a story where the CEO is a man and the secretary is a woman.”
- How to fix:
- Make prompts gender-neutral or inclusive.
- Use diverse names and roles.
- Test for bias by running prompts through different contexts and tweaking responses.
Tools like AI Fairness 360, Perspective API, and Bias Evaluator can help flag potential problems.
Keeping AI Use Transparent and Responsible
If you’re building AI tools or content, make it clear what parts were generated by machines. Misleading users can erode trust.
Best practices:
- Add AI disclosure statements in footers or metadata.
- Create ethical prompts that avoid deceptive or manipulative content.
- Avoid using AI to impersonate real people or spread misinformation.
Ethics aren’t an afterthought, they’re part of good prompt engineering.
Writing Prompts That Respect Privacy and Fairness
Avoid prompts that:
- Ask AI to generate personal data
- Guess identity, health, or finances
- Make speculative or defamatory claims
Also, don’t train AI on sensitive or private inputs. Always follow GDPR and data privacy laws, especially in B2B and enterprise projects.
Responsible prompt engineering isn’t just good practice, it’s your responsibility.
Prompt Engineering Portfolio Tips
What to Include in a Project Portfolio
Your portfolio is your proof of skill. Whether you’re looking for freelance gigs, full-time roles, or side hustle clients, your prompt portfolio should be clear, concise, and compelling.
Include:
- Project title + goal
- Before/after prompt results
- Tech stack (GPT, Claude, Gemini, etc.)
- Unique challenges you solved
- Screenshots or links to working demos
Bonus points for:
- Adding videos explaining your prompt logic
- Including prompt chains and workflows
- Showing performance metrics (like output quality or speed)
How to Present Your Prompts Effectively
Don’t just dump a bunch of prompts, tell a story.
For example: “I built a virtual tutor that adapts math explanations based on user age. I used few-shot prompting and temperature control to match tone.”
Use clean layouts:
- Google Docs
- Notion
- GitHub ReadMe
- Carrd or Webflow for personal sites
The easier your work is to understand, the more likely people will trust you with their AI needs.
Platforms to Showcase Your Work
- Use these platforms to make your portfolio visible:
- LinkedIn – Post case studies and mini-demos.
- GitHub – Great for tech-heavy or API-driven projects.
- PromptBase – Monetize your prompt templates.
- FlowGPT – Share and discover creative prompt flows.
- BuyMeACoffee or Gumroad – Sell prompt packs, tools, and guides.
Your portfolio isn’t just a resume, it’s a lead magnet. Make it work for you 24/7.
Conclusion
Prompt engineering in 2025 is where copywriting meets coding, and where creativity meets logic. Whether you’re a complete beginner or a tech enthusiast looking to specialize, the roadmap is clear:
- Learn the fundamentals.
- Practice daily.
- Build real projects.
- Stay curious, stay ethical, and never stop experimenting.
This field isn’t going away, it’s expanding. And those who learn how to “speak AI” fluently will be leading the next digital revolution.
FAQs
- Is coding required for prompt engineering?
Not necessarily. While knowing basic programming helps (especially with APIs), you can be an excellent prompt engineer using only no-code tools and platforms like ChatGPT or Notion AI. - Can I become a prompt engineer with no technical background?
Yes. Many prompt engineers come from writing, design, marketing, and teaching backgrounds. It’s about how well you communicate and structure tasks, not how well you code. - How long does it take to become proficient?
Most people can get good within 3–6 months with consistent daily practice and experimentation. - What’s the best way to practice daily?
Pick one task a day (e.g., summarize, explain, rewrite) and write 3–5 prompt variations for it. Track your progress in a journal or log. - Are certifications important for landing jobs in prompt engineering?
Certifications can help, but what matters most is your portfolio. Show real examples of how your prompts solve problems or automate tasks.
