AI tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini have changed the way we write, think, work, and create. But the real power of these tools lies in how you communicate with them and that comes down to one skill: prompt engineering.
When you ask AI a question, the way you phrase it can completely change the answer you get. That’s where prompt engineering comes in the art and science of crafting inputs to get the best possible outputs from AI models.
Think of it like talking to a super-smart but slightly literal-minded friend: if you don’t explain yourself clearly, they might go in the wrong direction. But with the right words, the results can be impressive, accurate, and exactly what you need.
In this article, we’ll break down Prompt Engineering 101: what it is, why it matters, and how you can start writing better AI prompts even if you’re a complete beginner.

What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the process of designing and refining instructions (called prompts) so an AI model, like ChatGPT, understands exactly what you want. This involves choosing the right words, structure, and context to produce reliable, high-quality responses.
Why Good Prompts Matter (Real Benefits You’ll Notice)
- Better accuracy – You get fewer “off-topic” answers.
- Time savings – Less editing, rewriting, and back-and-forth with the AI.
- More creativity – You can guide the model into producing unique, tailored results.
- Consistency – Repeatable, predictable outputs for similar queries.
If you’ve ever gotten an AI reply that made you think, “This isn’t what I meant at all,” then you’ve already felt the need for better prompt engineering.
Core Principles of Effective Prompts
Be Clear and Specific
Instead of saying,
“Write an article about space.”
Say:
“Write a 500-word, beginner-friendly blog post explaining black holes using simple analogies.”
The more precise you are, the better the AI can deliver.
Provide Relevant Context and Constraints
Context tells the AI what information to focus on. Constraints set boundaries for the result. For example:
“Create a table comparing the pros and cons of solar vs wind energy for small businesses in India.”
Ask for the Format You Want
Want bullet points, a table, or a story? Just say it. AI responds best to explicit instructions.
Use Explicit Roles and Personas
If you want expert-level insight, assign a role:
“Act as a senior UX designer reviewing a beginner’s portfolio.”
System vs. User vs. Assistant Messages
- System message: Sets the AI’s personality and overarching rules.
- User message: Your actual question or task.
- Assistant message: The AI’s response.
Good prompt design balances all three.
Prompting Techniques (Practical Patterns)
Zero-Shot, One-Shot, and Few-Shot Prompting
- Zero-shot: No examples, straight instructions.
- One-shot: One example to guide the style.
- Few-shot: Multiple examples for consistency.
Chain-of-Thought / Step-by-Step Prompting
Tell AI to think step-by-step. This improves reasoning and avoids rushed conclusions.
Example: “Explain your reasoning step-by-step before giving the final answer.”
Roleplay and Persona Prompts
Assigning roles makes AI adapt its tone and expertise. Example:
“You are an experienced fitness coach. Create a weekly workout plan for a busy beginner.”
Prompt Templates and Prompt Chaining
Templates save time for repeated tasks.
Chaining involves breaking a complex task into smaller prompts and feeding outputs back into the AI.
Scratchpad / Stepwise Chaining Example
- Generate a blog outline.
- Expand each section.
- Edit tone and style.
Model Parameters & Settings That Affect Prompts
Temperature, Top_p, and Creativity Control
- Temperature (0-1): Lower = more focused; higher = more creative.
- Top_p: Limits the “riskiness” of word choices.
When crafting prompts, key parameters shape how an AI responds. Temperature (0-1) adjusts creativity lower values yield precise, predictable answers, while higher values spark more imaginative outputs. Top_p narrows or widens the pool of possible word choices, controlling response “riskiness.”
Max Tokens and Token Budgets
More tokens = longer responses.
But too long can cut off mid-sentence.
Max tokens set the response length limit. More tokens allow longer answers, but overly long outputs risk mid-sentence cutoffs.
Context Window and Prompt Length Tradeoffs
Every model also has a context window its memory span. If prompts plus responses exceed it, older parts are forgotten, so keep input concise.
System Messages and Instruction Hierarchy
The system message usually overrides everything else. Use it wisely.
Finally, system messages guide behavior from the top down. They often override user prompts and set the tone, style, or role of the AI. Use them strategically to maintain consistency across outputs, especially for structured tasks like technical writing, storytelling, or brand voice adherence.
Iterative Workflows – Build Better Prompts Faster

A/B Testing & Metric-Driven Refinement
Test two prompt variations and see which performs better.
Debugging Prompts: Common Failure Modes
- AI misunderstands tone.
- AI includes irrelevant data.
- AI produces repetitive or generic answers.
Versioning Prompts and Reproducibility
Keep a prompt log so you can re-use the good ones.
Prompting for Specific Tasks
One of the strengths of prompt engineering is its adaptability. With the right wording, you can tailor AI to handle highly specific jobs across different fields. Here’s how prompting works in four common task categories.
Writing and Content Creation Prompts
AI can quickly generate blog posts, captions, ad copy, and more but only if your prompt sets the tone, style, and purpose clearly. For example:
“Write a friendly, 300-word Instagram caption about summer skincare tips with 5 hashtags.”
This tells the AI the platform, word count, tone, topic, and formatting needs. The more detail you provide, the less you’ll need to edit afterward.
Code Generation and Debugging Prompts
Developers can use prompts to generate scripts, fix bugs, or even explain code. For example:
“Write a Python script that scrapes headlines from BBC News and saves them to a CSV file.”
Adding language, functionality, and format in the prompt ensures the code meets your exact requirements. You can also ask AI to review existing code for bugs and suggest improvements.
Data Extraction, Summarization, and QA Prompts
AI excels at pulling information from documents and condensing it. For example:
“Summarize the attached PDF into 5 key bullet points.”
This works well for meeting notes, research papers, or long articles. Adding focus areas like “highlight only marketing strategies” makes summaries sharper and more relevant.
| Task Category | How Prompting Helps | Example Prompt |
|---|---|---|
| Writing & Content Creation | Defines tone, style, topic, length, and platform to reduce editing. | “Write a friendly, 300-word Instagram caption about summer skincare tips with 5 hashtags.” |
| Code Generation & Debugging | Specifies language, functionality, and output format; can also review and improve code. | “Write a Python script that scrapes headlines from BBC News and saves them to a CSV file.” |
| Data Extraction & Summarization | Pulls key insights from long texts; focus areas make results sharper and more relevant. | “Summarize the attached PDF into 5 key bullet points.” |
SEO, Marketing, and Conversion-Focused Prompts
Marketers can speed up campaign creation with prompts like:
“Generate 10 meta descriptions (under 160 characters) for an article about AI in education.”
Clear limits (character count) and goals (SEO) ensure the AI produces output ready for immediate use, helping you maintain brand voice while scaling content creation efficiently.
Tools, Libraries & Resources
Mastering prompt engineering isn’t just about creativity, it’s also about knowing the right tools and resources to refine, test, and scale your prompts effectively. Here are some of the most useful options for beginners and professionals alike.
Official Guides (OpenAI, Hugging Face)
If you want to truly understand how AI models think, start with the official documentation from leading AI providers.
- OpenAI Documentation offers detailed explanations of parameters, formatting, and best practices for working with ChatGPT and GPT models.
- Hugging Face Guides provide insights into a wide range of models, covering everything from transformers to fine-tuning techniques.
These resources are invaluable for learning model limitations, strengths, and advanced capabilities.
Community Prompt Libraries and Template Marketplaces
Sometimes, the best inspiration comes from what others have already tested.
- PromptBase – A marketplace for buying and selling high-quality, pre-tested prompts.
- FlowGPT – A community platform where users share prompts, rate them, and discuss improvements.
These libraries help you skip trial-and-error by building on proven prompt structures.
Editor Tools, Playgrounds, and Automated Testing
For hands-on experimentation:
- OpenAI Playground lets you tweak parameters, test variations, and see real-time changes in outputs.
- LangChain enables advanced workflows, such as chaining prompts, integrating APIs, and automating AI-driven processes.
By combining these tools with best practices, you can design, refine, and deploy prompts that consistently deliver high-quality results.
| Category | Examples | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Official Guides | OpenAI Docs, Hugging Face Guides | Learn parameters, formatting, model strengths & limits |
| Prompt Libraries | PromptBase, FlowGPT | Access pre-tested prompts, community sharing, inspiration |
| Editor & Testing Tools | OpenAI Playground, LangChain | Experiment, tweak parameters, automate workflows |
Common Mistakes & How to Fix Them
Even experienced users make prompt engineering mistakes that lead to confusing, inaccurate, or low-quality AI outputs. The good news? Most of these errors are easy to spot and fix once you know what to look for.
Vague Instructions
A prompt like “Write about marketing” is too broad, leaving the AI to guess your intent. The result will likely be generic.
Fix: Be explicit about topic, audience, style, and format. For example: “Write a 500-word beginner’s guide to social media marketing for small business owners, in a friendly and actionable tone.”
Too Many Tasks in One Prompt
Trying to get the AI to research, summarize, and write in one go often produces messy results.
Fix: Break the work into smaller, focused prompts. First, ask for research. Then, request a summary. Finally, ask for the final formatted output.
Not Testing Edge Cases
Most people test prompts only with “normal” inputs, but edge cases often reveal weaknesses.
Fix: Try “weird” or extreme inputs to see how the AI reacts. If it struggles, add clarifying constraints.
Over-Reliance on Single Phrasing
One wording might work most of the time, but AI performance can improve with variety.
Fix: Experiment with alternate phrasing, synonyms, and examples to see which version delivers the best consistency and quality.
Ethics, Safety & Robustness
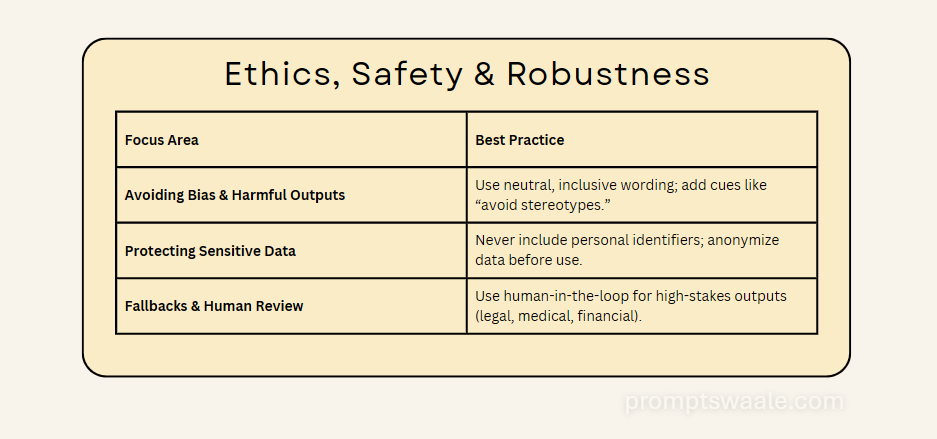
As AI becomes more embedded in daily life and business, ethical prompting is no longer optional, it’s essential. A well-crafted prompt isn’t just about getting the right output; it’s also about ensuring that output is safe, fair, and respectful.
Avoiding Bias and Harmful Outputs
AI can unintentionally reflect or amplify biases present in its training data. A careless prompt may produce stereotypes, discriminatory language, or culturally insensitive content. To reduce this risk, rephrase instructions to be neutral, inclusive, and context-aware. For example, instead of asking for “a typical businessman,” specify details without assumptions, such as “a professional in the finance industry.” Adding safety cues like “avoid stereotypes” can help guide the AI’s tone.
Protecting Private or Sensitive Data
Never include personal identifiers such as full names, phone numbers, medical records, or financial details in your prompts unless absolutely necessary and legally permitted. If you must work with sensitive data, anonymize it first. AI should be treated like a public environment where any information you enter could be exposed or stored.
Fallbacks and Human-in-the-Loop Safeguards
Even with careful prompting, AI can make mistakes or produce incomplete results. For high-stakes tasks like legal documents, medical advice, or financial recommendations always have a human reviewer verify the output. This “human-in-the-loop” approach ensures accuracy, ethical compliance, and trustworthiness before results are shared or implemented.
Future Trends in Prompting

FUTURE TRENDS IN PROMPTING
The field of prompt engineering is evolving rapidly, and the next wave of innovation is set to make AI interactions even more powerful and intuitive. Three major trends are shaping the future: multimodal prompts, agentic orchestration, and prompting as a recognized product skill.
Multimodal Prompts and Tool Use
Soon, prompts won’t be limited to just text. AI will handle multimodal inputs meaning you can combine text, images, audio, and even video in a single request. Imagine uploading a photo of a room, describing your preferred style, and asking the AI to redesign it while also generating a shopping list. This ability to blend formats will open the door to more natural, real-world problem-solving.
Agentic Prompts and Orchestration
We’re moving toward AI systems that can act autonomously with a chain of linked tasks. Instead of giving one instruction at a time, you’ll be able to set a high-level goal and let the AI break it into smaller steps, execute them, and report back. This orchestration will make AI feel more like a proactive assistant than a passive tool.
Prompting as a Product Skill
As AI integrates into business workflows, prompt engineering will become a core job skill, much like web development today. Companies will need professionals who can design precise, efficient prompts that deliver measurable results making prompt engineers highly sought-after in tech, marketing, education, and beyond.
Practical Prompt Templates & 20+ Examples
When you have a good prompt template, you don’t have to start from scratch every time. Templates help you save time, ensure consistency, and get predictable results, no matter what the task is. Below are five powerful templates along with multiple examples you can directly adapt to your needs.
Template 1: “Act as [role] and create [output] for [audience], with [style] tone, in [format].”

Why it works:
By assigning a role, you tell the AI what perspective or expertise to take. Adding the audience ensures the content is tailored, while specifying tone and format controls the style and structure.
Structure Breakdown:
- Role: Who the AI should “be” (expert, blogger, coach, marketer, etc.).
- Output: What to produce (article, script, report, ad copy).
- Audience: Who it’s for (students, CEOs, beginners).
- Style: Formal, casual, humorous, persuasive.
- Format: Bulleted list, table, blog post, social media caption.
Examples:
- “Act as a personal finance expert and write a 1,000-word guide for millennials on how to start investing, in a conversational tone, formatted as a step-by-step article.”
- “Act as a professional resume writer and create a CV for a software developer with 5 years’ experience, in a clean and modern format.”
- “Act as a dietician and prepare a 7-day meal plan for a vegetarian athlete, in a friendly tone, using a table format.”
- “Act as a social media strategist and write 10 Instagram captions for a coffee shop, using a witty tone and emojis.”
Template 2: “Summarize [content] into [length] focusing on [key points].”
Why it works:
Summarization prompts help the AI filter out irrelevant details and focus only on what matters. By setting a target length and focus area, you avoid vague, unfocused summaries.
Structure Breakdown:
- Content: The source (article, transcript, PDF).
- Length: Specific word count, bullet points, or sentence limit.
- Focus: The exact topics or themes to emphasize.
Examples:
- “Summarize this research paper into 200 words focusing on the methodology and results.”
- “Summarize this YouTube transcript into 5 bullet points highlighting the main marketing tips.”
- “Summarize this 3,000-word blog post into a 10-point checklist for busy readers.”
- “Summarize the meeting notes into a 1-paragraph action plan focusing on deadlines and responsibilities.”
Template 3: “Generate [number] variations of [item] for [purpose].”
Why it works:
This is perfect for brainstorming, idea generation, and testing multiple creative options. You can compare the variations and pick the best.
Structure Breakdown:
- Number: How many versions you want.
- Item: The type of content (title, slogan, headline, email subject).
- Purpose: The end goal (SEO, conversion, branding).
Examples:
- “Generate 15 blog post titles about AI tools for small businesses that are SEO-friendly.”
- “Generate 10 slogan ideas for an eco-friendly cleaning product that sound catchy and modern.”
- “Generate 8 email subject lines for a summer sale to boost open rates.”
- “Generate 12 ad headlines for a new fitness app that targets busy professionals.”

Template 4: “Explain [topic] to a [audience] using [teaching method].”
Why it works:
AI can explain concepts at different difficulty levels. By setting the audience and teaching method, you make the explanation engaging and easy to understand.
Structure Breakdown:
- Topic: The concept or process.
- Audience: Age, profession, or skill level.
- Teaching Method: Analogy, storytelling, step-by-step guide.
Examples:
- “Explain blockchain to a high school student using a school library analogy.”
- “Explain photosynthesis to a 5-year-old using a short story about plants drinking sunlight.”
- “Explain machine learning to a marketing team using real-life business examples.”
- “Explain quantum computing to a beginner programmer using a step-by-step tutorial format.”
Template 5: “List [number] [ideas/examples/tips] for [goal].”
Why it works:
Lists are quick to scan, easy to share, and perfect for brainstorming or inspiration.
Structure Breakdown:
- Number: Specific quantity for structure.
- Ideas/Examples/Tips: The type of list items.
- Goal: The objective or problem to solve.
Examples:
- “List 20 YouTube video ideas for a cooking channel that focuses on budget-friendly recipes.”
- “List 10 ways to increase website traffic for a small online store.”
- “List 15 creative Instagram reel ideas for a travel agency.”
- “List 25 blog post ideas for a fitness website targeting beginners.”
Pro Tip: You can combine these templates for more control. For example:
“Act as a social media strategist and list 15 Instagram reel ideas for a vegan bakery in a playful tone, formatted in a table with captions and hashtags.”
Conclusion
Prompt engineering isn’t just about talking to AI, it’s about talking to AI well. The clearer, more structured, and more thoughtful your instructions are, the better your results will be. By mastering prompt engineering, you’ll save time, improve accuracy, and unlock far more creative possibilities.
Remember: AI is powerful, but it’s only as good as the instructions you give it. Treat it like a skilled but literal minded teammate, guide it clearly, and it will deliver.
FAQs
1. What’s the difference between prompt engineering and normal prompting?
Prompt engineering is a deliberate process of designing, testing, and refining prompts for better results, not just typing in a question.
2. Can I use the same prompt for different AI models?
Yes, but results may vary. Some models need slight adjustments in wording.
3. How long should my prompt be?
As short as possible while still including all necessary details and context.
4. Do I need coding skills for prompt engineering?
No, but for advanced automation and chaining, coding can help.
5. What’s the biggest mistake beginners make?
Being too vague : always be clear about what you want, how you want it, and for whom.